 Thanks to a large body of scientific research, there are many options for breast augmentation today as compared to 35 years ago. There are choices in types of implant filler (saline or silicone), location of incisions, position of implant pocket, and choice of implant shape. These options are discussed in detail at the in-person appointment. The decisions regarding the options for breast augmentation are made by the patient after the informed consent process is completed.
Thanks to a large body of scientific research, there are many options for breast augmentation today as compared to 35 years ago. There are choices in types of implant filler (saline or silicone), location of incisions, position of implant pocket, and choice of implant shape. These options are discussed in detail at the in-person appointment. The decisions regarding the options for breast augmentation are made by the patient after the informed consent process is completed.
One decision that the patient will make is the position of the implants. When referring to the position of the implants, this means the position of the implants in relation to the breast gland and the chest muscles. The placement of the breast implants can be sub-mammary (below the breast gland and above the muscle), sub-fascial (above the muscle and below the breast gland and the muscle covering (fascia)), partially sub-muscular (partially below the muscle and partially below the breast gland), or totally sub-muscular (completely below the muscle).
One of the factors in determining the placement of the breast implants is the thickness of the breast plate (breast tissue). The thickness of the breast plate can be estimated with the “pinch test.” The “pinch test” is done by pinching the breast above the nipple-areolar complex and measuring the thickness with a Boley gauge or other measuring device. The breast measurement found in this manner helps determine if the implants are placed “above” or “below” the muscle(s).
There are advantages and disadvantages to both “above” and “below” the muscle placement that are explained during the informed consent process. The thickness of the breast tissue is used as a guideline and is only one of many factors that are considered for surgical planning and recommendations. The thickness that is generally considered as the “break point” is 2.0 centimeters. Again, the 2.0 centimeter thickness is only a single guideline and not a binding rule.
In the patients below, the “pinch test” is demonstrated and measured with a Boley gauge. In Patient 1, the breast plate is very thin, making the recommendation lean towards a “below” the muscle procedure. (Again, there are other factors to consider in addition to the breast plate thickness.)
Patient 1
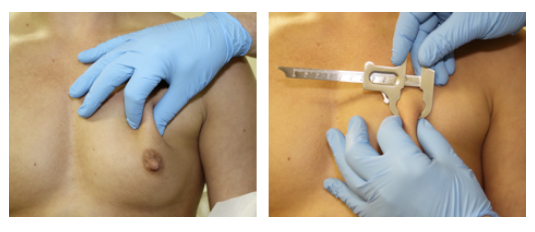
In Patient 2, the breast plate is slightly thicker, but is still relatively thin, making the recommendation lean towards a “below” the muscle plane.
Patient 2
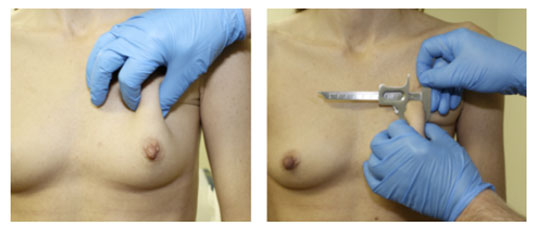
In Patient 3, the breast plate is much thicker, making the “above” the muscle procedure a reasonable option if the patient so desires.
Patient 3
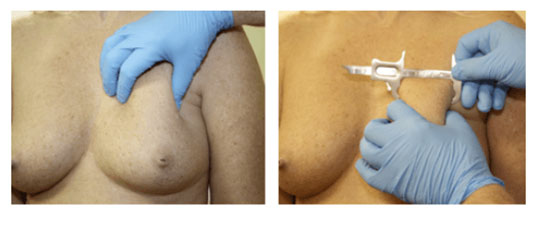
Ultimately, it is the patient that chooses the position of the breast implants. In summary, there are many factors that help determine if the breast implants are placed above or below the muscle(s)—the “pinch test” being only one. The “pinch test” and many other parameters are explained and discussed at the in-person consultation.
For more information about breast implant placement, or if you are interested in breast augmentation and wish to schedule a consultation, please don’t hesitate to contact Stephen Herring, MD today. Dr. Herring is a board-certified plastic surgeon renowned for his personal approach to breast augmentation. Whether you live locally or are traveling from out of town, he is happy to help!
Previous Post Next Post